A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Kidney Stones with Ayurveda and Modern Medicine
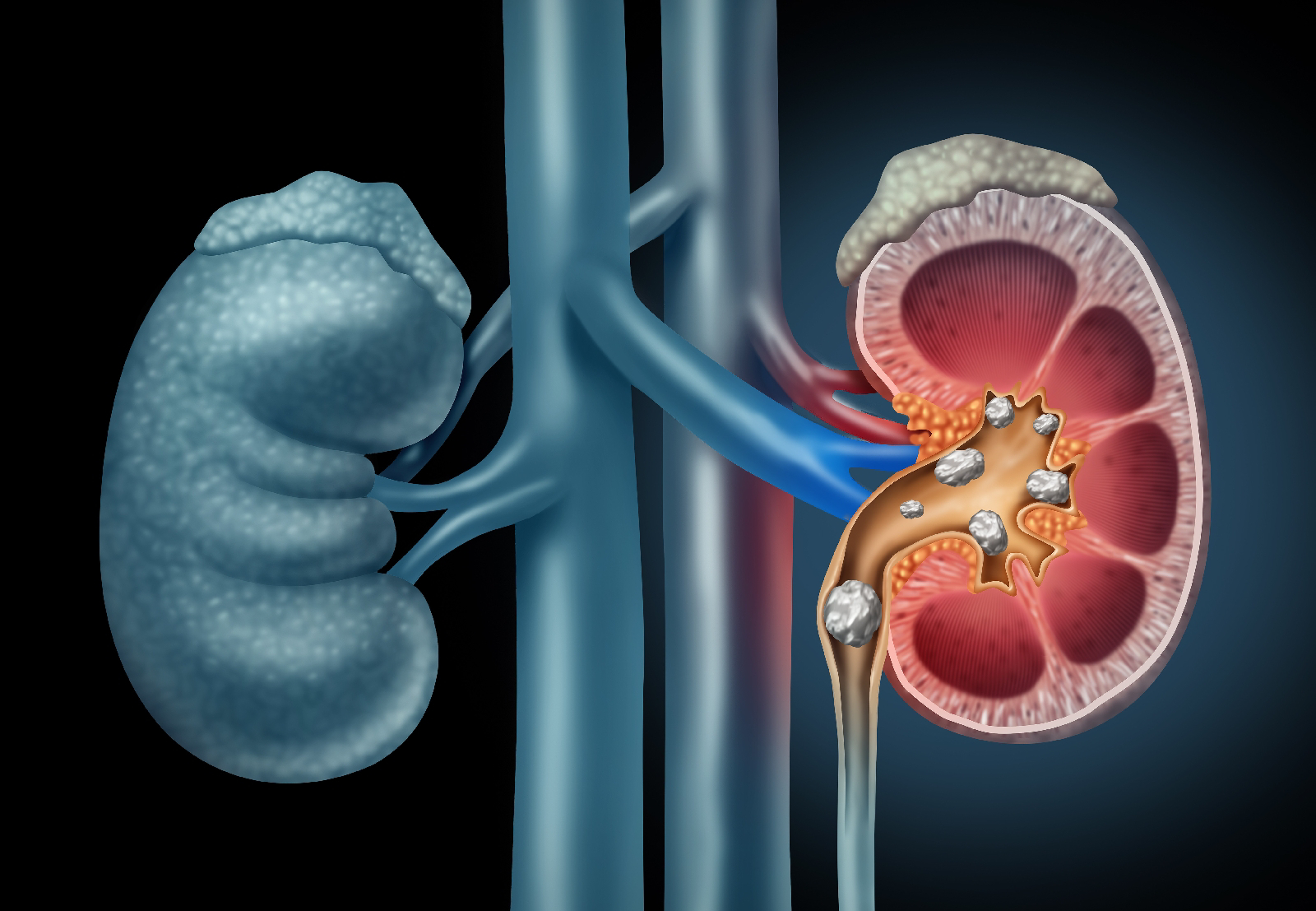
Kidney stones, also known as nephrolithiasis, are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. They can cause severe pain and complications if not managed properly. In this guide, we will explore both modern and Ayurvedic approaches to treating and preventing kidney stones, providing you with a holistic perspective on managing this condition.
Understanding Kidney Stones
Causes of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones form when minerals in the urine crystallize and stick together. Several factors can increase the risk of developing stones:
1. Dehydration: Insufficient water intake can lead to concentrated urine, making it easier for minerals to crystallize.
2. Diet: High intake of oxalate-rich foods (e.g., spinach, beets, nuts), high protein consumption, excessive salt, and sugar can contribute to stone formation.
3. Genetics: Family history of kidney stones can increase the likelihood of developing them.
4. Medical Conditions: Conditions like gout, hyperparathyroidism, and urinary tract infections can increase the risk.
5. Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and calcium-based antacids, can contribute to stone formation.
Types of Kidney Stones
1. Calcium Oxalate Stones: The most common type, formed when calcium binds with oxalate in the urine. Causes include high oxalate foods, dehydration, and certain metabolic disorders.
2. Uric Acid Stones: Formed due to high levels of uric acid, often linked to a high-protein diet, gout, and genetic factors.
3. Struvite Stones: Associated with urinary tract infections, these stones can grow quickly and become quite large.
4. Cystine Stones: Result from a genetic disorder causing cystine to leak into the urine and form crystals.
Modern Medical Treatments
1. Medications
a. Pain Relievers
- Examples: Ibuprofen, acetaminophen.
- Mechanism of Action: Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Dose: Ibuprofen 400-800 mg every 6-8 hours as needed.
- Duration: Until pain subsides.
- Effects: Pain relief, reduced inflammation.
- Side Effects: Gastrointestinal issues, kidney damage with long-term use.
b. Alpha Blockers
- **Examples**: Tamsulosin.
- **Mechanism of Action**: Relax the muscles in the ureter, facilitating the passage of stones.
- **Dose**: 0.4 mg once daily.
- **Duration**: Generally used for a few weeks.
- **Effects**: Easier passage of stones.
- **Side Effects**: Dizziness, headache, fatigue.
c. Potassium Citrate
- **Mechanism of Action**: Alkalinizes urine, helping to dissolve uric acid stones and prevent formation of calcium stones.
- **Dose**: 10-20 mEq 2-3 times daily.
- **Duration**: Long-term for prevention.
- **Effects**: Reduced stone formation and dissolution of uric acid stones.
- **Side Effects**: Gastrointestinal upset, high potassium levels.
2. Non-Invasive Treatments
a. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)**
- **Mechanism of Action**: Uses shock waves to break stones into smaller pieces that can be passed in urine.
- **Dose**: One or more sessions.
- **Duration**: Outpatient procedure lasting about 30-60 minutes.
- **Effects**: Stones are broken into smaller fragments.
- **Side Effects**: Hematuria, bruising, discomfort.
3. Invasive Procedures
a. Ureteroscopy
- **Mechanism of Action**: A thin tube with a camera is inserted through the urethra to remove or break up stones.
- **Dose**: Procedure-specific; performed under anesthesia.
- **Duration**: Outpatient procedure lasting 30-60 minutes.
- **Effects**: Removal or fragmentation of stones.
- **Side Effects**: Urinary tract infection, bleeding, discomfort.
b. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
- **Mechanism of Action**: Surgical procedure where a small incision is made in the back to remove large stones.
- **Dose**: Requires general anesthesia.
- **Duration**: 1-2 hours; hospitalization for a few days.
- **Effects**: Direct removal of stones.
- **Side Effects**: Bleeding, infection, pain.
Ayurvedic Approach to Kidney Stones
Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine, offers a holistic approach to managing kidney stones, focusing on balancing the body's doshas (vital energies) and supporting urinary health.
1. Herbal Remedies
a. Chandraprabha Vati
- **Mechanism of Action**: Helps dissolve stones and improve urinary function.
- **Dose**: 1-2 tablets, 2-3 times daily, after meals.
- **Duration**: 6-8 weeks, or as advised by the practitioner.
- **Effects**: Stone dissolution, improved urinary health.
- **Side Effects**: Generally well-tolerated; some may experience gastrointestinal discomfort.
b. Cystone
- **Mechanism of Action**: Contains a blend of herbs that help in breaking down and expelling stones. It also supports overall kidney health and helps prevent recurrence.
- **Dose**: 2 tablets, 2-3 times daily.
- **Duration**: 6-8 weeks, or as advised by the practitioner.
- **Effects**: Assists in stone dissolution, promotes urinary health, and helps prevent future stones.
- **Side Effects**: Usually well-tolerated; potential mild gastrointestinal issues.
c. Gokshuradi Guggulu
- **Mechanism of Action**: Combines herbs that help in reducing the size of stones and improving kidney function.
- **Dose**: 1-2 tablets, 2-3 times daily.
- **Duration**: 6-8 weeks, or as advised by the practitioner.
- **Effects**: Supports stone dissolution and promotes urinary tract health.
- **Side Effects**: Generally well-tolerated; possible mild digestive issues.
d. Pashanbheda (Powder)
- **Mechanism of Action**: Known for its lithotriptic (stone-breaking) and diuretic properties, aiding in the dissolution and elimination of stones.
- **Dose**: 500 mg to 1 g, 2-3 times daily.
- **Duration**: 6-8 weeks.
- **Effects**: Facilitates the breakdown and expulsion of stones.
- **Side Effects**: Rare; may include mild gastrointestinal discomfort.
2. Panchakarma Therapies
a. Abhyanga (Oil Massage)
- **Mechanism of Action**: Enhances circulation and promotes detoxification.
- **Frequency**: 2-3 times per week.
- **Instructions**: Use warm sesame or coconut oil; massage gently.
b. Basti (Enema Therapy)
- **Mechanism of Action**: Cleanses the colon and supports kidney function.
- **Frequency**: Weekly or as advised by the practitioner.
- **Instructions**: Use medicated oil or decoctions under the guidance of an Ayurvedic therapist.
3. Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations
- **Increase Fluid Intake**: Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily to help flush out stones and prevent dehydration.
- **Avoid High-Oxalate Foods**: Limit foods such as spinach, beets, and nuts.
- **Include Diuretic Foods**: Eat foods like watermelon, cucumber, and celery that support urine flow.
- **Reduce Salt Intake**: Minimize consumption of salty foods.
- **Regular Exercise**: Engage in moderate physical activity such as walking or yoga to improve overall health and support kidney function.
- **Stress Management**: Practice stress-relief techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
Ayurvedic Prescription for Nephrolithiasis
Combining all these approaches, here’s a comprehensive Ayurvedic prescription for managing nephrolithiasis:
1. Herbal Medicines
- Chandraprabha Vati: 1-2 tablets, 2-3 times daily, after meals, for 6-8 weeks.
- Cystone: 2 tablets, 2-3 times daily, for 6-8 weeks.
- Gokshuradi Guggulu: 1-2 tablets, 2-3 times daily, for 6-8 weeks.
- Pashanbheda (Powder): 500 mg to 1 g, 2-3 times daily, for 6-8 weeks.
2. Panchakarma Therapies
- Abhyanga: Oil massage 2-3 times per week using warm sesame or coconut oil.
- Basti: Enema therapy weekly or as advised by the practitioner.
3. Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water and include diuretic foods in your diet.
- Diet: Avoid high-oxalate foods and reduce salt intake.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity.
- Stress Management: Practice meditation or other stress-relief techniques.
Conclusion
Managing kidney stones requires a comprehensive approach that includes both modern medical treatments and traditional Ayurvedic practices. By combining these methods, you can effectively manage and prevent kidney stones, improving your overall urinary health and quality of


Comments
Post a Comment